- Infertility is a disease of the male or female reproductive system defined by the failure to establish a
clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse. (World Health
Organization, 2022). - Affects approximately 15% of couples worldwide who are wishing to conceive, which means roughly
1 in 6 couples experience some form of infertility. - When an etiology is identified, infertility cases can be attributed to female factors (~30%), male
factors (~30%), or a combination of both (~40%). However, a considerable number of cases remain
unexplained and are classified as “idiopathic infertility” (~30%)(Carson et al., 2021). - Genetic defects contribute significantly to infertility cases, affecting both males and females equally
(Krausz, 2011).
What are the Infertility Panels?
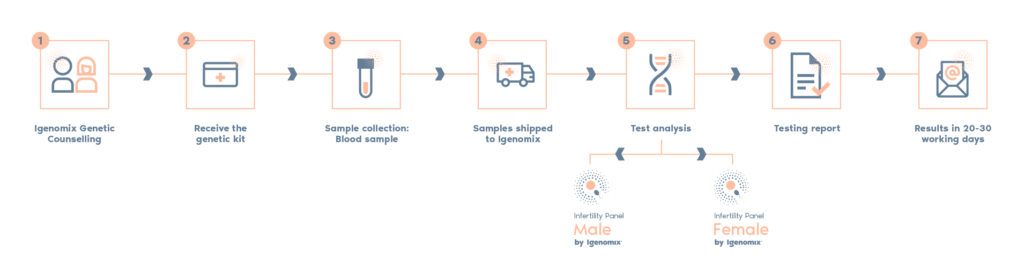
- The Infertility Panel is a simple blood/saliva test designed to detect the most common genetic
mutations associated with monogenic infertility in both male and female. - Our panel includes genes with confirmed disease-associated variants related to infertility disorders
separately in males or females. - The Igenomix Infertility Panels can be used to make a directed and accurate differential diagnosis of
inability to conceive ultimately leading to a better management and achieve a healthy baby at home.
What is the procedure?
The test utilizes Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology with whole exome-based sequencing
to conduct a comprehensive analysis of genes associated with fertility issues. Additional testing to
analyse frequent infertility disease-causing variants not detected using NGS technology will be
conducted by alternative methods.
Only genes with confirmed disease-associated variants related to infertility disorders were included
in the panel, which were referred to as "diagnostic genes".
The genes were divided into two sub-panels: a Female fertility panel and a Male fertility panel.